Automated Vulnerability Remediation Explained: Best Practices for Reducing Real-World Risk

Why Automated Vulnerability Remediation Is Critical for Modern Enterprises
Enterprise security teams today are under immense pressure to remediate thousands of vulnerabilities generated by a growing number of scanners across infrastructure, applications, and cloud. Manual processes—built on spreadsheets, emails, and inconsistent ticketing—don’t scale. They delay action, increase operational fatigue, and leave critical systems and sensitive data exposed.
Automated vulnerability remediation has emerged as a strategic solution for scalable security operations. By combining exploitability insights, business context, and automated remediation workflows, it empowers teams to fix what matters first and reduce security risks more effectively.
What Is Automated Vulnerability Remediation?
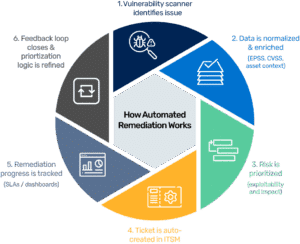
Automated vulnerability remediation refers to the orchestration of data, logic, and workflows to detect, prioritize, assign, and resolve vulnerabilities without relying solely on manual intervention.
A typical implementation includes:
- Ingesting findings from multiple vulnerability scanners
- Enriching data with EPSS, CVSS, asset criticality, and threat intelligence
- Automatically generating remediation tickets in ITSM platforms (e.g., Jira, ServiceNow)
- Monitoring progress against defined SLAs
- Reporting on remediation coverage and risk reduction
This approach transforms fragmented remediation workflows into a streamlined, measurable vulnerability remediation process.
Comparison: Manual vs. Automated Vulnerability Remediation
| Feature | Manual Remediation | Automated Remediation |
|---|---|---|
| Prioritization | CVSS-based, manual triage | Risk-based (EPSS, business impact) |
| Workflow | Spreadsheets, email | ITSM-integrated workflows |
| Speed | Reactive, delayed | Proactive, real-time |
| Consistency | Human error-prone | Standardized and repeatable |
| Visibility | Siloed and limited | Real-time dashboards and SLA tracking |
Why Manual Remediation No Longer Works
Security teams still relying on manual processes face several recurring challenges:
- Too many findings with no standardized prioritization logic
- Inconsistent or delayed assignment of remediation tasks
- Siloed tools and communication gaps between security and IT teams
- Lack of visibility into remediation timelines and results
The result? Increased exposure, reduced accountability, and missed opportunities to fix critical vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Core Components of an Automated Remediation Program
Effective automation requires more than scripts and workflows. It must be grounded in visibility, intelligence, and alignment with organizational risk.
1. Centralized and Normalized Vulnerability Data
Consolidate findings from all scanners (infrastructure, application, and cloud) into a unified platform. Normalize data to eliminate inconsistencies and create a shared context for prioritization.
2. Risk-Based Prioritization Logic
Use exploit prediction models (e.g., EPSS), asset exposure, business impact, and threat intelligence to determine what to fix first. Prioritization based solely on CVSS is no longer sufficient—EPSS and CVSS-based prioritization together provide better accuracy.
3. Seamless ITSM Integration
Automatically assign remediation tasks to the right teams through integrated ITSM platforms. Maintain clear accountability, track SLA adherence, and eliminate manual ticket creation for automated patching or fixes.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
Use dashboards and analytics to track remediation performance and refine prioritization rules. Monitor mean time to remediation (MTTR), SLA breaches, recurring vulnerabilities, and trends across security remediation efforts.
Real-World Example: Nestlé’s Approach to Scalable Remediation
Nestlé implemented Brinqa to orchestrate risk-based remediation at scale. With more than 2,000 business units and hundreds of thousands of findings, Nestlé needed a solution that could prioritize intelligently and automate ticketing.
Key outcomes:
- Critical vulnerabilities were prioritized and resolved faster
- Tickets were automatically created and routed to appropriate IT teams
- Global risk visibility improved through real-time dashboards and SLA tracking
This approach led to a measurable reduction in exposure and operational fatigue.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is automated vulnerability remediation?
Automated vulnerability remediation is the use of technology and workflows to detect, prioritize, assign, and resolve security vulnerabilities without relying solely on manual processes.
Why is manual remediation insufficient for modern security teams?
Manual remediation is time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale. It often leads to delayed response times, fragmented workflows, and increased exposure to critical vulnerabilities.
What are the benefits of automating vulnerability remediation?
Benefits include reduced mean time to remediation (MTTR), improved SLA adherence, better alignment between security and IT operations, and decreased operational fatigue.
What tools are used in automated remediation workflows?
Organizations use scanners, ITSM platforms like Jira or ServiceNow, threat intelligence feeds, and automated prioritization models such as EPSS. These tools form the core of automated vulnerability management systems.
How does Brinqa support automated vulnerability remediation?
The Brinqa automated vulnerability remediation solution consolidates vulnerability data, applies risk-based prioritization, automates ticket creation, and tracks remediation outcomes through dashboards and SLA monitoring.
How do you automate vulnerability remediation?
To automate vulnerability remediation, begin by integrating scanners with a centralized platform that supports EPSS-based risk modeling and ITSM integration. Automate ticket creation for high-risk findings and monitor remediation workflows through dashboards.
Top Metrics to Track in Automated Remediation
| Metric | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| MTTR (Mean Time to Remediate) | Tracks efficiency of remediation workflows |
| SLA Compliance | Ensures adherence to internal policies |
| % of Critical Vulns Resolved | Measures actual risk reduction |
| Reopen Rates | Detects recurring or failed fixes |
| Ticket Aging | Surfaces bottlenecks in IT ops handoffs |
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Even with automation, remediation programs can fall short if:
- Prioritization is based solely on CVSS without EPSS or asset context
- False positives and incomplete data lead to wasted cycles
- Automation lacks governance or stakeholder buy-in
- There’s no continuous monitoring of risk and performance
Effective automation requires clean data, clear policies, and active oversight.
How Brinqa Helps
Brinqa enables automated, risk-based remediation at scale by:
- Aggregating and normalizing findings from all vulnerability sources
- Applying configurable prioritization logic that includes EPSS, business context, and exposure
- Integrating with ITSM platforms to automate task assignment and tracking
- Providing dashboards for SLA monitoring, compliance, and reporting
With Brinqa, organizations reduce response time, improve operational efficiency, and ensure remediation efforts align with risk.
You can learn more about the foundational principles behind this approach in our companion post on Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM).
Taking the Next Step Toward Scalable Risk Reduction
Automated vulnerability remediation is more than a workflow enhancement—it’s a strategic capability. By applying intelligence and orchestration to remediation processes, security teams can reduce exposure, accelerate resolution timelines, and make more meaningful progress against their cyber risk goals.
With the right platform and approach, automation empowers teams to focus on fixing what matters most. Request a demo of Brinqa to see how our unified vulnerability and exposure management platform can help you protect what matters most.