Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Explained: How to Prioritize What Matters Most

Why Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Is Essential for Modern Enterprises
Enterprise security teams today are overwhelmed by the volume of vulnerabilities across cloud, infrastructure, and application environments. With limited time and resources, fixing everything is impossible — and trying to do so often leads to operational fatigue and missed threats.
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) is a modern approach that helps organizations prioritize vulnerabilities based on real-world risk — not just severity scores. It uses exploit intelligence, business context, and asset exposure to determine which issues actually pose the greatest threat to your organization.
In this post, we’ll explain what RBVM is, why it’s essential, and how leading enterprises like Nestlé, Cambia Health, and SAP are using it to modernize their vulnerability management programs.
Defining Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) is a strategic framework that prioritizes vulnerabilities not by technical severity alone, but by their potential impact on the organization. It integrates data from multiple vulnerability scanners, threat intelligence sources, and asset inventories to provide a unified, contextual view of risk.
RBVM enables security teams to:
- Focus remediation efforts on vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk (i.e., they are both exploitable and impactful)
- Avoid wasting resources on low-priority technical findings
- Align vulnerability management processes with business risk and compliance objectives
Unlike traditional approaches, this risk-based approach acknowledges that not all vulnerabilities are equal—especially in complex environments where patching capacity is constrained.
Traditional vs. Risk-Based Vulnerability Management: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Traditional VM | Risk-Based VM |
|---|---|
| CVSS-only prioritization | Context-aware prioritization (EPSS + business risk) |
| Manual ticketing | Automated remediation workflows |
| Fragmented data | Centralized platform |
| Limited reporting | Real-time dashboards & SLAs |
Why Organizations Are Moving Beyond CVSS
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) has served as a useful baseline for assessing technical severity, but it lacks real-world context. CVSS does not account for:
- Whether a vulnerability is currently being exploited in the wild
- Whether the vulnerable asset is exposed to the internet
- The criticality of the asset to business operations
- The presence of compensating controls
Relying on CVSS risk scores alone can lead to inefficient remediation workflows and missed opportunities to mitigate actual risk. RBVM addresses these limitations by applying risk-based prioritization models that reflect the full threat landscape.
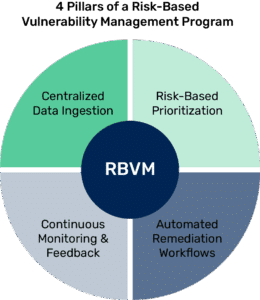
Core Pillars of an Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Program
Efficient and effective implementation of RBVM requires four foundational capabilities:
1. Centralized Data Ingestion and Normalization
RBVM begins with visibility. Organizations must collect and normalize vulnerability findings from multiple scanners (e.g., Qualys, Tenable, Rapid7) as well as asset inventories, CMDBs, cloud platforms, and security tools. This creates a consistent and centralized dataset for prioritization and reporting.
2. Risk-Based Prioritization
RBVM prioritizes vulnerabilities using multiple contextual signals:
- Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS): Measures the probability of exploitation within 30 days
- Business context: Considers asset criticality, data classification, and SLA requirements
- Threat intelligence: Includes knowledge of known exploits, ransomware toolkits, and active campaigns
- Exposure: Evaluates whether affected systems are externally accessible or segmented
This approach enables organizations to focus on the vulnerabilities that truly increase security risks—rather than chasing every high-severity finding.
3. Automated Remediation Workflows
A key benefit of RBVM is the ability to streamline remediation processes. Mature programs automate:
- Ticket creation and routing based on risk thresholds
- SLA monitoring and escalation
- Reporting to IT, DevOps, and business stakeholders
Automated workflows ensure that critical vulnerabilities are addressed quickly, while reducing the administrative burden on security and operations teams.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
RBVM is not a one-time project. It requires continuous vulnerability assessment, telemetry integration, and feedback loops to reflect changes in threat activity, asset inventories, and business priorities. The most mature organizations go further with penetration testing and attack path analysis for validating controls.
What’s Driving RBVM Adoption
Security leaders are increasingly embracing RBVM to overcome the following challenges:
- High volumes of scanner findings: Most organizations can only remediate a fraction of what they discover
- Lack of remediation ownership: It’s often unclear who is responsible for fixing a given vulnerability
- Tool sprawl and siloed data: Disparate systems make it difficult to correlate risk across the organization
- Attack surface growth: With expanding cloud, third-party, and API integrations, vulnerabilities are harder to detect and prioritize
- Board-level accountability: CISOs must demonstrate risk reduction, not just compliance
Real-World RBVM in Action: Case Studies
Leading enterprises have adopted RBVM to modernize their vulnerability management programs. Here are three examples featured in Brinqa’s RBVM framework:
Nestlé
- Centralized vulnerability management across 2,000 business units, replacing spreadsheets
- Used Brinqa to calculate risk ratings and auto-generate remediation tickets
- Achieved 3x faster patching cycles for high-priority vulnerabilities
Cambia Health
- Shifted from spreadsheets to a unified risk-based program
- Incorporated business and asset context into remediation logic, reducing discovery and remediation time by 50%
- Reduced time-to-fix and increased visibility into security vulnerabilities
> Read the Cambia Health case study.
SAP
- Operates 70,000 running systems globally
- Reduced manual, error-prone, time consuming spreadsheet-based VM tracking and reporting
- Prioritizes vulnerabilities resulting in 2-3x team productivity enhancements
Key Benefits of Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
Organizations that implement risk-based vulnerability management solutions report significant improvements across multiple metrics:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Improved Security Posture | Reduced exposure to active and high-impact vulnerabilities |
| Faster Remediation | Reduced mean time to remediation (MTTR) for critical issues |
| Operational Efficiency | Fewer manual processes and reduced alert fatigue |
| Executive Reporting | Risk dashboards for leadership, audit, and compliance reviews |
| Technical Debt Reduction | Minimized accumulation of unresolved findings |
How Brinqa Enables Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
Brinqa offers a purpose-built RBVM platform designed for complex enterprise environments. Key capabilities include:
- Data consolidation and normalization across scanners, assets, threat intel, and business systems
- Risk modeling using configurable logic and exploit prediction models like EPSS and threat intelligence
- Automated workflows for remediation, escalation, and SLA tracking
- Dashboards and reports for CISOs, risk owners, and compliance teams
By unifying vulnerability, asset, and threat data into one platform, Brinqa provides the visibility and automation necessary to operationalize RBVM at scale.
Getting Started with RBVM
Organizations can adopt a risk-based approach to vulnerability management by:
- Identifying existing vulnerability scanners and asset inventories
- Defining criteria for prioritizing high-risk vulnerabilities
- Centralizing data into a single analytics platform
- Automating remediation and reporting workflows with ticketing system integrations
- Reviewing outcomes and refining risk models over time
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is risk-based vulnerability management?
A: Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) is a strategic approach that prioritizes vulnerabilities based on exploitability, asset exposure, and business impact.
Q: How is RBVM different from traditional vulnerability management?
A: RBVM goes beyond CVSS by incorporating threat intelligence, exploit prediction (e.g., EPSS), asset criticality, and business context to prioritize vulnerabilities more effectively.
Q: Why is RBVM important for enterprise security teams?
A: RBVM helps security teams focus on high-risk vulnerabilities, improve remediation efficiency, and demonstrate measurable risk reduction to executives and auditors.
Q: What are the key components of an RBVM program?
A: Key components include centralized vulnerability data, risk-based prioritization logic, automated remediation workflows, and continuous risk monitoring.
Q: Which organizations are using RBVM effectively?
A: Enterprises like Nestlé, Cambia Health, and SAP have successfully implemented RBVM to reduce exposure and operational risk.
A Smarter Approach to Reducing Security Risk
Risk-based vulnerability management enables organizations to make smarter decisions about what to fix, when, and why. In an era where security teams are inundated with data and constrained by resources, RBVM delivers clarity, precision, and measurable risk reduction.
Learn how Brinqa can help by requesting a personalized demo of our unified vulnerability and exposure management platform.